1、概述
对于插件化框架 Hook 机制是一个核心,那到底 Hook 是什么呢?怎么去理解插件化中的 Hook呢?在我看来插件化中的 Hook 机制就是通过反射注入和动态代理来实现的。
先来说说何为反射注入,大家都知道依赖注入,其实反射注入算是依赖注入的一种,顾名思义,通过反射的方式将依赖对象注入目标对象。举个例子,想要替换掉 ActivityThread 中的 mInstrumentation:
/*android.app.ActivityThread.java*/
public final class ActivityThread {
Instrumentation mInstrumentation;
public static ActivityThread currentActivityThread() {
return sCurrentActivityThread;
}
...
}
//Instrumentation代理类
public class InstrumentationDelegate extends Instrumentation {
private Instrumentation base;
public InstrumentationDelegate(Instrumentation base) {
this.base = base;
}
}
public class ReflectInject{
public void reflectInject() throws Exception {
// 根据全类名获取Class
Class activityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
// 获取无参的currentActivityThread函数
Method currentActivityThreadMethod = activityThreadClass.getMethod("currentActivityThread");
// 调用currentActivityThread函数获取当前ActivityThread对象
currentActivityThreadMethod.setAccessible(true);
Object currentActivityThreadObject = currentActivityThreadMethod.invoke(null);
// 获取mInstrumentation字段
Field instrumentationField = activityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mInstrumentation");
// 破坏封装获取对象
instrumentationField.setAccessible(true);
Object instrumentationObject = instrumentationField.get(null);
// 注入Instrumentation代理对象
if(!(instrumentationObject instanceof InstrumentationDelegate)) {
instrumentationField.set(activityThreadClass, new InstrumentationDelegate((Instrumentation)instrumentationObject));
}
}
}以上就是对于 mInstrumentation 的反射注入,当然凭借封装可以有更优雅的实现,这里为了方便展示过程粗暴直接。
关于动态代理大家可以参考彻底理解 Java 动态代理这篇文章,写得十分清晰。文章最后也提到了动态代理的局限性,动态代理无法支持对于非接口的类进行代理,所以在 Hook 时一般结合静态代理来特殊处理需要代理的类,比较典型的例子是 android.app.Instrumentation 的代理。好在 Android 系统服务大都通过 Binder 机制来实现的,而 Binder 机制的 C/S 架构对于接口的支持天然的好,这对于整个 Hook 框架中代理类实现的工作量来说就大大的减少了。
2、Hook 框架
我们知道 Hook 本身依赖反射机制,从上面示例上也可以看出,直接使用大量反射导致代码可读性、维护性变得非常差,从代码美观可读性、易维护性上来看,一个可读性强易维护的 Hook 框架显得尤为重要,目前众多开源的插件化框架中 VirtualApp 的 Hook 框架是最优秀的。为什么这么说呢,作者使用了基于注解的反射注入技术,合理的框架设计使得虽然 Hook 的对象非常多,代码却井井有条,不得不赞叹作者 lody 的巧妙构思,让人受益良多。
以下分析基于 master 分支 c493161 版本。
2.1 设计类图
又到了祭出法宝的时候了,废话不多说先看设计类图:
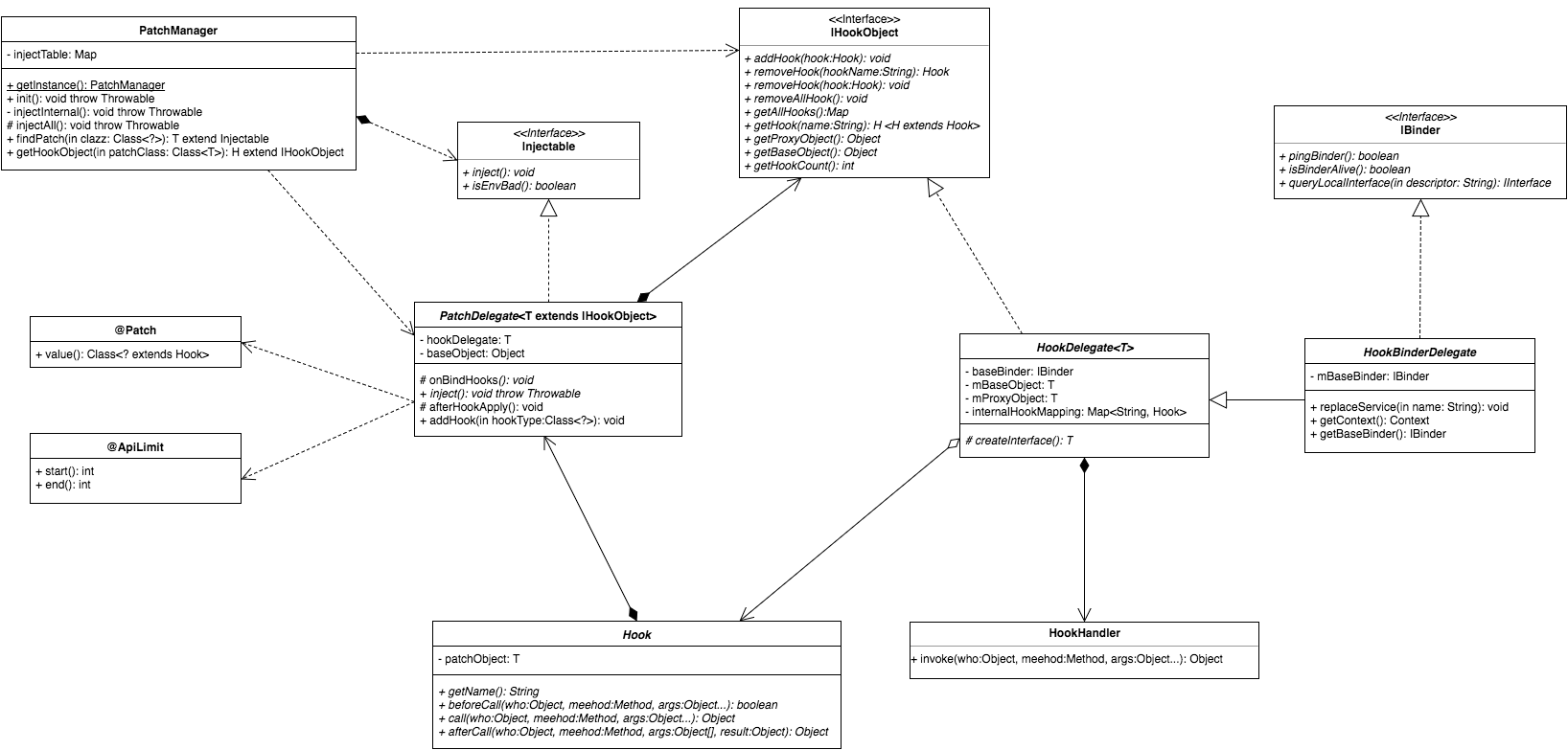
2.2 类图解析
首先作者设计了两个接口,一个是 Injectable ,这个接口比较简单,使实现这个接口的类都具备的注入的能力;
public interface Injectable {
void inject() throws Throwable;
boolean isEnvBad();
}另一个是 IHookObject ,使实现这个接口的类具备管理代理类的 Hook 函数能力。
public interface IHookObject {
void copyHooks(IHookObject from);
MapgetAllHooks();
Hook addHook(Hook hook);
Hook removeHook(String hookName);
void removeHook(Hook hook);
void removeAllHook(); H getHook(String name);
Object getProxyInterface();
Object getBaseInterface();
int getHookCount();
}上面我们提到了 Hook 函数这个概念,怎么理解这个概念呢,因为动态代理的调用是函数级别的,所以 Hook 相当于替换函数实现。再来看 Hook 这个抽象类,这个类定义了 Hook 的处理时机,以及提供一些 Hook 环境的依赖,实现类通过指定代理函数名,可以根据需要在 beforeCall 、call 、 afterCall 执行逻辑处理。所以, Hook 的实现类可以理解为代理函数的类象化。
public abstract class Hook {
private boolean enable = true;
public abstract String getName();
public boolean beforeCall(Object who, Method method, Object... args) {
return true;
}
public Object call(Object who, Method method, Object... args) throws Throwable {
return method.invoke(who, args);
}
public Object afterCall(Object who, Method method, Object[] args, Object result) throws Throwable {
return result;
}
public boolean isEnable() {
return enable;
}
public void setEnable(boolean enable) {
this.enable = enable;
}
...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hook${ " + getName() + " }";
}
}来看看抽象类 HookDelegate ,它是 IHookObject 的接口实现,在构造中通过 HookHandler完成了动态代理,内部维护了 Hook 集合,代码如下。
public abstract class HookDelegateimplements IHookObject {
private static final String TAG = HookDelegate.class.getSimpleName();
private T mBaseInterface;
private T mProxyInterface;
/**
* 内部维护的Hook集合
*/
private MapinternalHookMapping = new HashMap();
@Override
public MapgetAllHooks() {
return internalHookMapping;
}
public HookDelegate(Class... proxyInterfaces) {
// 获取接口,完成动态代理
mBaseInterface = createInterface();
if (mBaseInterface != null) {
if (proxyInterfaces == null) {
proxyInterfaces = HookUtils.getAllInterface(mBaseInterface.getClass());
}
mProxyInterface = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mBaseInterface.getClass().getClassLoader(), proxyInterfaces, new HookHandler());
} else {
VLog.d(TAG, "Unable to build HookDelegate: %s.", getClass().getName());
}
}
public HookDelegate() {
this((Class[]) null);
}
protected abstract T createInterface();
@Override
public void copyHooks(IHookObject from) {
this.internalHookMapping.putAll(from.getAllHooks());
}
// 添加 Hook 函数
@Override
public Hook addHook(Hook hook) {
if (hook != null && !TextUtils.isEmpty(hook.getName())) {
if (internalHookMapping.containsKey(hook.getName())) {
VLog.w(TAG, "Hook(%s) from class(%s) have been added, can't add again.", hook.getName(),
hook.getClass().getName());
return hook;
}
internalHookMapping.put(hook.getName(), hook);
}
return hook;
}
...
/**
* @return 包装后的代理对象
*/
@Override
public T getProxyInterface() {
return mProxyInterface;
}
/**
* @return 原对象
*/
@Override
public T getBaseInterface() {
return mBaseInterface;
}
...
private class HookHandler implements InvocationHandler {
// 动态代理,通过函数名找到对应的 Hook 函数,完成 beforeCall、call、afterCall 的调用
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Hook hook = getHook(method.getName());
try {
if (hook != null && hook.isEnable()) {
if (hook.beforeCall(mBaseInterface, method, args)) {
Object res = hook.call(mBaseInterface, method, args);
res = hook.afterCall(mBaseInterface, method, args, res);
return res;
}
}
return method.invoke(mBaseInterface, args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getTargetException();
if (cause != null) {
throw cause;
}
throw e;
}
}
}
}对于 HookBinderDelegate 这个类,继承自 HookDelegate 扩展了 IBinder 接口,借此方便处理系统 Binder 服务的代理。
public abstract class HookBinderDelegate extends HookDelegateimplements IBinder {
private IBinder mBaseBinder;
public HookBinderDelegate(Class... proxyInterfaces) {
super(proxyInterfaces);
init();
}
public HookBinderDelegate() {
super();
init();
}
private void init() {
mBaseBinder = getBaseInterface() != null ? getBaseInterface().asBinder() : null;
addHook(new AsBinder());
}
//此处通过反射替换系统服务
public void replaceService(String name) {
if (mBaseBinder != null) {
ServiceManager.sCache.get().put(name, this);
}
}
//这里Hook asBinder函数,使该函数调用后返回代理Binder对象。
private final class AsBinder extends Hook {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "asBinder";
}
@Override
public Object call(Object who, Method method, Object... args) throws Throwable {
return HookBinderDelegate.this;
}
}
...
public Context getContext() {
return VirtualCore.get().getContext();
}
...
@Override
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) {
return getProxyInterface();
}
...
public IBinder getBaseBinder() {
return mBaseBinder;
}
}接在在来看 PatchDelegate 这个抽象类,它是 Injectable 的接口实现,依赖 @Patch及 @ApiLimit 注解将 Hook 类的添加进 Hook 集合;它的泛型为 IHookObject ,这就意味着 HookDelegate HookBinderDelegate 的实现类很容易通过泛型约束,并通过 inject 接口完成注入。
public abstract class PatchDelegateimplements Injectable {
protected T hookDelegate;
protected Object baseObject;
public PatchDelegate() {
this(null);
}
public PatchDelegate(Object baseObject) {
attachInterface(baseObject);
}
protected void attachInterface(Object baseObject) {
this.baseObject = baseObject;
this.hookDelegate = createHookDelegate();
onBindHooks();
afterHookApply(hookDelegate);
}
protected abstract T createHookDelegate();
protected void onBindHooks() {
if (hookDelegate == null) {
return;
}
// 通过 @Patch、@ApiLimit 注解将 Hook 函数添加至代理类的 Hook 集合
Class clazz = getClass();
Patch patch = clazz.getAnnotation(Patch.class);
int version = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
if (patch != null) {
Class[] hookTypes = patch.value();
for (Class hookType : hookTypes) {
ApiLimit apiLimit = hookType.getAnnotation(ApiLimit.class);
boolean needToAddHook = true;
if (apiLimit != null) {
int apiStart = apiLimit.start();
int apiEnd = apiLimit.end();
boolean highThanStart = apiStart == -1 || version > apiStart;
boolean lowThanEnd = apiEnd == -1 || version < apiEnd;
if (!highThanStart || !lowThanEnd) {
needToAddHook = false;
}
}
if (needToAddHook) {
addHook(hookType);
}
}
}
}
private void addHook(Class hookType) {
try {
Constructor constructor = hookType.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
Hook hook;
if (constructor.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
hook = (Hook) constructor.newInstance();
} else {
hook = (Hook) constructor.newInstance(this);
}
hookDelegate.addHook(hook);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instance Hook : " + hookType + " : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public Hook addHook(Hook hook) {
return hookDelegate.addHook(hook);
}
protected void afterHookApply(T delegate) {
}
@Override
public abstract void inject() throws Throwable;
public Context getContext() {
return VirtualCore.get().getContext();
}
public T getHookDelegate() {
return hookDelegate;
}
}最后再来说说 PatchManager ,这个类顾名思义就知道是补丁的管理类,在这里将各个 Patch 完成注入。
public final class PatchManager {
private static final String TAG = PatchManager.class.getSimpleName();
private Map<class, Injectable> injectTable = new HashMap<>(12);
private PatchManager() {
}
public static PatchManager getInstance() {
return PatchManagerHolder.sPatchManager;
}
void injectAll() throws Throwable {
for (Injectable injectable : injectTable.values()) {
injectable.inject();
}
// XXX: Lazy inject the Instrumentation,
// It is important in many cases.
addPatch(AppInstrumentation.getDefault());
}
public boolean isInit() {
return PatchManagerHolder.sInit;
}
public void init() throws Throwable {
if (PatchManagerHolder.sInit) {
throw new IllegalStateException("PatchManager Has been initialized.");
}
injectInternal();
PatchManagerHolder.sInit = true;
}
private void injectInternal() throws Throwable {
if (VirtualCore.get().isMainProcess()) {
return;
}
if (VirtualCore.get().isServerProcess()) {
addPatch(new ActivityManagerPatch());
addPatch(new PackageManagerPatch());
return;
}
if (VirtualCore.get().isVAppProcess()) {
addPatch(new LibCorePatch());
addPatch(new ActivityManagerPatch());
addPatch(new PackageManagerPatch());
addPatch(HCallbackHook.getDefault());
//以下省略诸多Path
...
}
}
private void addPatch(Injectable injectable) {
injectTable.put(injectable.getClass(), injectable);
}
publicT findPatch(Classclazz) {
// noinspection unchecked
return (T) injectTable.get(clazz);
}
publicvoid checkEnv(Classclazz) {
Injectable injectable = findPatch(clazz);
if (injectable != null && injectable.isEnvBad()) {
try {
injectable.inject();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
publicH getHookObject(ClasspatchClass) {
T patch = findPatch(patchClass);
if (patch != null && patch instanceof PatchDelegate) {
// noinspection unchecked
return (H) ((PatchDelegate) patch).getHookDelegate();
}
return null;
}
private static final class PatchManagerHolder {
private static PatchManager sPatchManager = new PatchManager();
private static boolean sInit;
}
}2.3 过程梳理
如果感觉以上内容不好理解的话,下面的这幅图,可能会缓解这种不适感。

以 AccountManagerService Hook 为例,①、② 两步将 AccountBinderDelegate 等 Binder 代理注入至 ServiceManager ,假设触发 ③ getService 获取 AccountManagerService 后,调用 ④ getPwd ,这时 ⑤ getPwd 将通过 HookHandler 动态代理调用到代理类 ⑥ getHook 查找到函数代理对象,然后 ⑦ invoke 完成 Hook 函数 即 getPassword 代理调用。
到这里,整个 Hook 框架大致上就说完了。当然诸多版本的 Rom(官方、第三方)适配还是一个庞大的工作量,这就体现了作者对整个 Android Framework 掌握的功力了,这里额外提一下,作者对于Framework 镜像的处理,也是相当的精妙,这也为整个 Hook 框架的代码可读性贡献了相当一部分的力量,详见项目的 mirror 包 。
3、最后的闲扯
在阅读源码以及优秀开源项目的时候,大多数人都会感到很难读的通,我的一个看法和切身体会是,就像你第一眼看到一个人,肯定感觉十分陌生,而相处过一段时间后,这种陌生感就会慢慢消失,进而你反而会很了解她,知道她的爱好,知道她喜欢吃什么。阅读源码也是这样,短时间内如果无法拿下,又很想理解它,那么就要多花些时间,去读,不断的读和理解,了解源码所涉及的知识,尝试去用自己的理解去揣摩作者的思路,这个期间你需要用适合自己学习的方式(比如画类图,流程图、时序图,只要这种方式对你是有效的不必拘泥于形式)去记录修正你的理解,不断的去逼近作者的想法和思路,这也是一个学习成长的过程。
道阻且长,行则将至。that’s all.
温馨提示:文章内容系作者个人观点,不代表博观网对观点赞同或支持。
版权声明:本文为转载文章,来源于 solart ,版权归原作者所有,欢迎分享本文,转载请保留出处!





 鄂公网安备 42018502001427号
鄂公网安备 42018502001427号
发表评论